

A man travels for nine months alone with great wealth and has nothing to fear. Ibn Battuta, a 14th-century Muslim traveler, described the function of a caravenserai in the region of China:Ĭhina is the safest and best country for the traveller. Urban versions of caravanserais also became important centers of economic activity in cities across these different regions of the Muslim world, often concentrated near the main souq areas, with many examples still standing in the historic areas of Damascus, Aleppo, Cairo, Istanbul, Fes, etc. the large Sultan Han in Aksaray Province) as well as in Iran (e.g. A number of 12th to 13th-century caravanserais or hans were built throughout the Seljuk Empire, many examples of which have survived across Turkey today (e.g. Throughout most of the Islamic period (7th century and after), caravanserais were a common type of structure both in the rural countryside and in dense urban centers across the Middle East, North Africa, and Ottoman Europe. History Ĭorral del Carbón, a former caravanserai in Granada, Spain The term khan was also frequently used for this type of building in Egypt. The word wikala means roughly "agency" in Arabic, in this case a commercial agency, which may also have been a reference to the customs offices that could be located here to deal with imported goods. The Arabic word wikala (وكالة), sometimes spelled wakala or wekala, is a term found frequently in historic Cairo for an urban caravanserai which housed merchants and their goods and served as a center for trade, storage, transactions and other commercial activity. In the cities of this region such buildings were also frequently used as housing for artisan workshops. : 116 The word comes from Greek pandocheion, lit.: "welcoming all", thus meaning 'inn', led to funduq in Arabic ( فندق), pundak in Hebrew ( פונדק), fundaco in Venice, fondaco in Genoa and alhóndiga or fonda in Spanish ( funduq is the origin of Spanish term fonda). The church, consulate and arsenal have been removed (although it still remains possible to obtain cannons/artillery through the consulate).The term funduq ( Arabic: فندق sometimes spelled foundouk or fondouk from the French transliteration) is frequently used for historic inns in Morocco and around western North Africa. The outpost and the artillery foundry are replaced by the castle which combines these two buildings. In the same way, farms and the plantations are both replaced by a building called rice field, which allows the player to infinitely collect either gold or food. The saloon, a building to recruit mercenaries introduced in Age of Empires III: The WarChiefs, has been replaced by a monastery for the new civilizations.
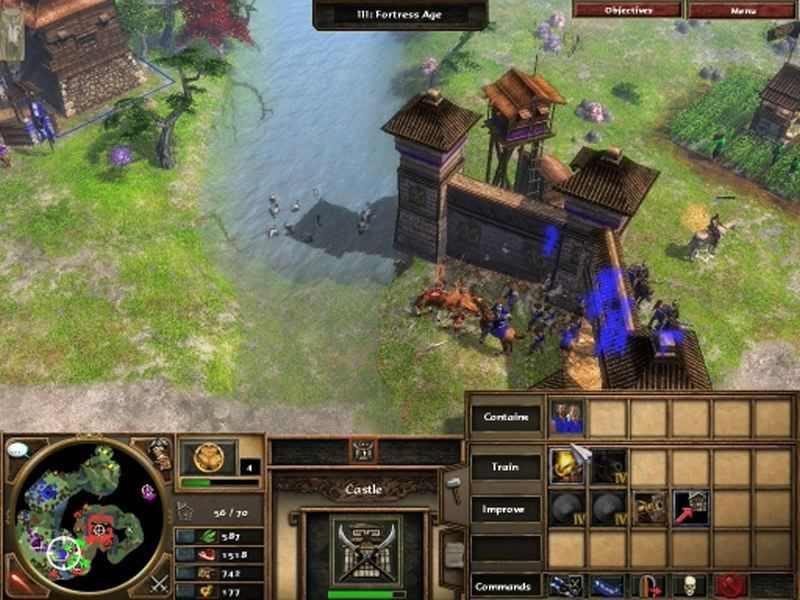
New additions to the gameĪpart from the three new civilizations, the list of buildable buildings by villagers has undergone a reshuffle. For each of the Asian civilizations, the player can build a unique consulate, which allows you to ally with a European nation (French, English, Dutch, Spaniards, Germans, Portuguese, Ottomans, Russians), each bringing bonuses in exchange for export points, a resource automatically generated by each villager. This new expansion pack was released in the fall of 2007.
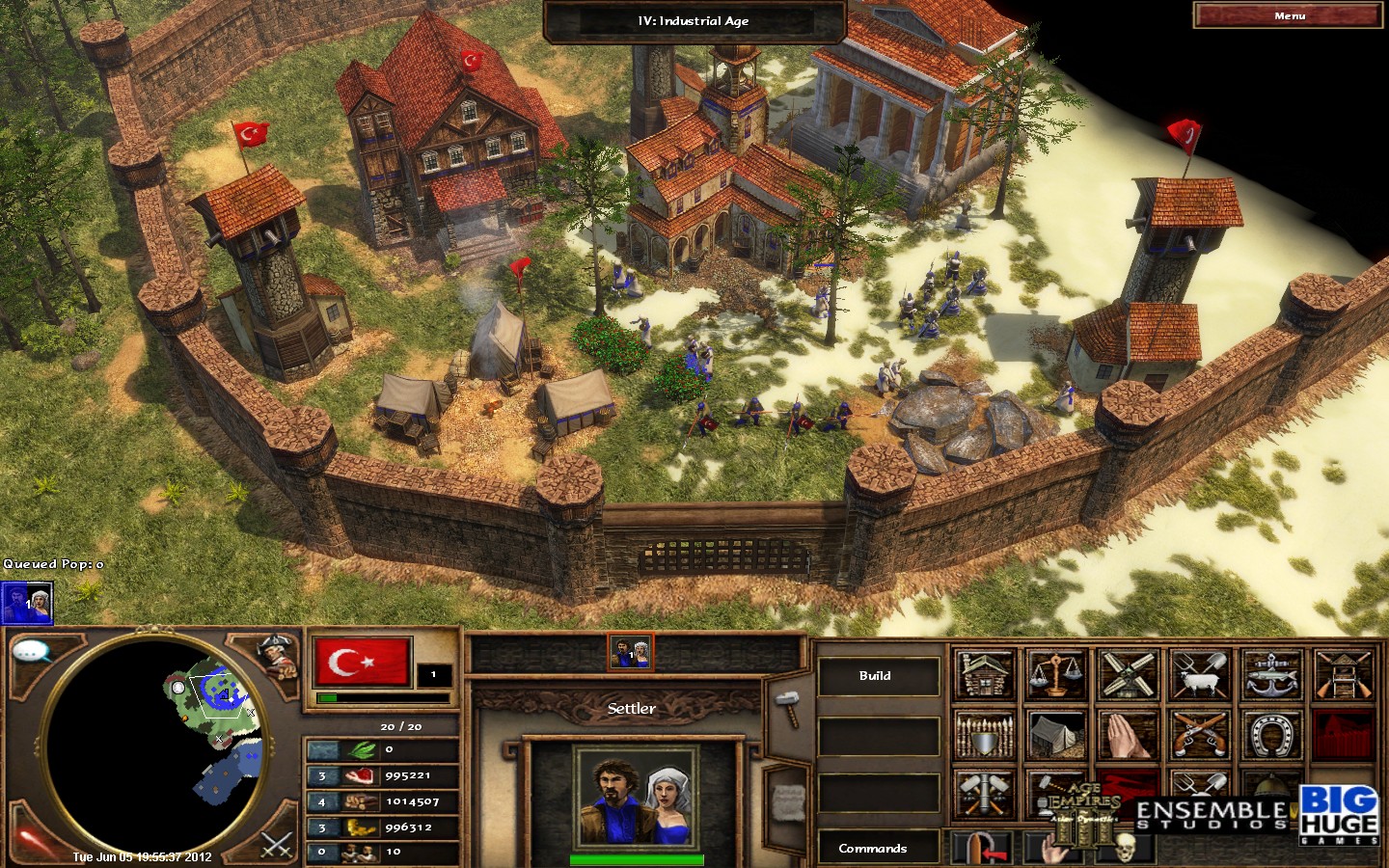
The game also contains three new campaigns divided into five scenarios, each representing one of the new Asian civilizations. These civilizations bring a total of 15 new wonders, each of them bringing improvements and making it possible to progress to the next age. Three new Asian civilizations are introduced, the Chinese, Japanese and Indians. Beyond the new world, players can now explore the Asian continent. Age of Empires III: The Asian Dynasties is the second expansion pack of Age of Empires III developed by Big Huge Games.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
